TallyPrime Performance – Errors & Resolutions
Cause 1: You have enabled multiple Gateway Servers in your computer.
Resolution: Disable the unused Tally Gateway Servers from your computer.
- Click the Windows icon > Run > type services.msc, and press Enter.
- Locate the instance of Tally Gateway Server that you want to disable, right-click the instance > select Properties.
- Click Stop to change the Service status to Stopped.
- Under Startup type, select Disabled, and click Stop > and click Apply.
Cause 2: Absence of tallyprime.lic and Tally Gateway Servers.
Resolution: If TallyPrime is in Educational Mode, you can check the availability of tallyprime.lic. After that, you can then select an active license or reactivate your existing license to use TallyPrime in license mode.
To check the availability of tallyprime.lic:
- Right-click the TallyPrime Shortcut on your desktop.
- Click Open file location.
- Check for tallyprime.lic among the the other files in the folder. If tallyprime.lic is not present, it might have caused the TallyPrime application to open in the educational mode.
Scenario – 1
If TallyPrime opens in Educational mode, you can use license from network or select an active license to use your TallyPrime license.
To select an active license,
- Press F1 (Help) > Settings > License > Manage License > Show Active Licenses Only.
- Select the licenses with active status.
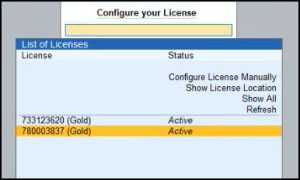
- Select Yes to continue.
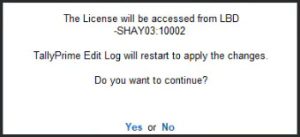
TallyPrime will restart and use the correct Gateway Service to fetch the license.
Scenario – 2
If your license has gone into Educational Mode, you can reactivate your TallyPrime license.
Disable the unused Tally Gateway Servers from your computer.
- Click the Windows icon > Run > type services.msc, and press Enter.
- Locate the instance of Tally Gateway Server that you want to disable, right-click the instance > select Properties.

- Click Stop to change the Service status to Stopped.

- Under Startup type, select Disabled, and click Stop > and click Apply.
Cause 3: In case there are several companies to be loaded on startup, opening all the companies on starting TallyPrime might take time, depending on the volume of your data.
Resolution: You can set the option Load companies on startup to No, if you have already enabled the option and selected a Company to load after you open TallyPrime.
- Open the Startup Settings screen: Press F1 (Help) > Settings > Startup.
- Set the option Load companies on startup to No.
In case you must load companies on starting TallyPrime, select only the most required companies to load on startup to avoid any possibilities of performance issue.
Cause 4: If you have been using third-party firewalls for network security, you might have Internet latency (speed) issue.
Resolution: To resolve issues related to Internet latency (speed), you can whitelist some of the URLs or hostnames and IP addresses in your Firewall or Proxy settings. To do this, you have to identify the required IP addresses or URLs for the services you need and add IP Addresses, URLs, and Hostnames to Windows Proxy or Firewall Exceptions List. To add ports to Windows Firewall Exceptions List and add TallyPrime Data Extensions in Antivirus Exceptions List, refer to the Add TallyPrime EXE and Ports to Firewall Exceptions List topic.
However, you can also do one of the following scenarios to check/identify if there is an issue with the Internet latency (speed) issue:
Scenario 1:
- Click the Search icon appearing on the Taskbar of your computer.
- Search for Command Prompt and press Enter.
- In the Command Prompt, type ping tallynet.tallyenterprise.com -t and press Enter.
If you can see repeated requests getting typed in the screen, then your request is not reaching the server.
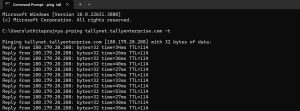
In such a case, you can reconnect with the network by connecting with the IP service provider or System Admin to resolve the network connectivity issue.
Scenario 2:
- Click the Search icon appearing on the Taskbar of your computer.
- Search for Command Prompt and press Enter.
- In the Command Prompt, type ping tallynet.tallyenterprise.com and press Enter.
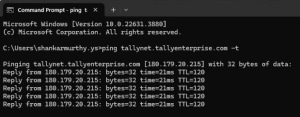
If you can see repeated requests getting typed in the screen, then your request is not reaching the server. In such a case, you can reconnect with the network by connecting with the IP service provider or System Admin to resolve the network connectivity issue.
Scenario 3:
- Click the Search icon appearing on the Taskbar of your computer.
- Search for Command Prompt and press Enter.
- In the Command Prompt, type nslookup tallynet.tallyenterprise.com and press Enter.
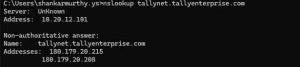
You can see your IP Address. Display of your IP Address implies that the command has successfully reachedtallynet.tallyenterprise.com, and the communication is happening .
Cause 1:
Low bandwidth or unstable network communication between the client and server.
Resolution:
Ping speed variation should be minimal, ideally between 1 ms and 3 ms which is the minimum accepted network variation. Ensure that the network speed is always uniform between the client and the server systems. Any difference in the link speed affects the transfer of data between the client and server system.
For example, when the link speed is 100 Mbps, and the transfer rate is 56 Mbps, the performance of data over the network will be slow. You also need to ensure that the network speed should be 60 Mbps from node to server and server to node systems.
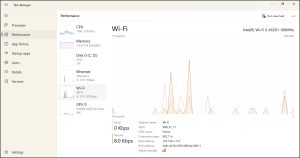
To view the link speed:
- In your computer, right-click on your bottom bar and select Task Manager.
- Select Performance. The graph displays the network and link speed for the system.
- Check Network latency from Command Prompt.
- Click the Search icon appearing on the Taskbar of your computer.
- Search for Command Prompt and press Enter.
- Write the command ping server name -t and press Enter.
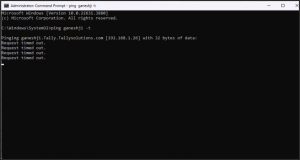
This instant communication displays ‘Request timed out’ which means you will not be able to access data or your data access will be slow.
For latest Windows systems, click Performance in Task Manager to view the network speed.
Cause 2:
You are using different system configurations for RAM, Processor, and Operating Systems, such as Windows 10, Windows7, Windows XP, and so on.
Resolution:
To resolve issues related to system configurations, ensure that you use the same system configurations across all the nodes. For example, if a computer has 4 GB RAM with 2.1 GHz processor with Windows 10 Operating System, same configuration has to be used across all the nodes.
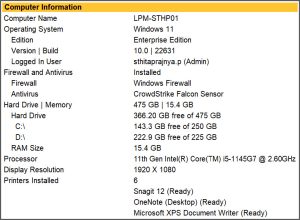
To check system configuration from TallyPrime, press F1 (Help)> About > Computer Information.
For Single user or Server system:
Cause 1:
RAM configuration is different across all the node systems.
Resolution:
Same RAM configuration should be used in all the node systems. For example, if a system has 4 GB RAM with 2.1 GHz processor with Windows 10 Operating System, same configuration to be used across all the nodes.
To check system configuration from TallyPrime, press F1 (Help)> About > Computer Information.
Cause 2:
Different versions of Windows Operating System used across all the node systems.
Resolution:
Windows operating system version should be same in all the node systems. For example, if you are using Windows 10 in one node, then all the systems should have Windows 10.
Cause 3:
Processor speed is different across all the node systems.
Resolution:
Processor speed should be same in all the node systems. If the processor speed is 2.3 Ghz in one node, then the other node systems should also have the same processor speed.
Cause 4:
Existing customisations require additional validation during the voucher entry.
Resolution:
Try to open the voucher after deselecting the account TDLs/Add-ons and disabling the local TDLs.
Cause 5:
Memory consumption increases during the voucher entry, primarily due to the higher data size, which is influenced by the company’s features and the volume of data stored in that company.
Resolution:
Delete the Masters of the company if there are no other masters or transactions using it and try opening the voucher again in TallyPrime. In TallyPrime, you can also view and delete multiple unused masters at once.
In client systems/Node:
Cause 1:
RAM configuration is different across all the node systems.
Resolution:
Same RAM configuration should be used in all the node systems. For example, if a system has 4 GB RAM with 2.1 GHz processor with Windows 10 Operating System, same configuration to be used across all the nodes.
To check system configuration from TallyPrime, press F1 (Help)> About > Computer Information.
Cause 2:
Different versions of Windows Operating System used across all the node systems.
Resolution:
Windows operating system version should be same in all the node systems. For example, if you are using Windows 10 in one node, then all the systems should have Windows 10.
Cause 3:
Processor speed is different across all the node systems.
Resolution:
Processor speed should be same in all the node systems. If the processor speed is 2.3 Ghz in one node, then the other node systems should also have the same processor speed.
Cause 4:
Existing customisations require additional validation during the voucher entry.
Resolution:
Try to make the voucher entry after deselecting the account TDLs/Add-ons and disabling the local TDLs.
Cause 5:
Memory consumption increases during the voucher entry, primarily due to the higher data size, which is influenced by the company’s features and the volume of data stored in that company.
Resolution:
Delete the Masters of the company if there are no other masters or transactions using it and try opening the voucher again in TallyPrime. In TallyPrime, you can also view and delete multiple unused masters at once.
Cause 6:
Type of network such as LAN or WIFI will impact the navigation time during the voucher entry.
Resolution:
Switch the network and try again.
Cause 7:
Slow network speed
Resolution:
Network Speed should be high for example, either 100 Mbps/1Gbps.
Cause 8:
Network cable or the category of cables used, such as Cat 5 or Cat 6/7.
Resolution:
Opt for a cable with higher category value.
Cause 9:
Low bandwidth or unstable network communication between the client and server.
Resolution:
Ping speed variation should be minimal, ideally between 1 ms and 3 ms which is the minimum accepted network variation. Ensure that the network speed is always uniform between the client and the server systems. Any difference in the link speed affects the transfer of data between the client and server system.
For example, when the link speed is 100 Mbps, and the transfer rate is 56 Mbps, the performance of data over the network will be slow. You also need to ensure that the network speed should be 60 Mbps from node to server and server to node systems.
To view the link speed:
- In your computer, right-click on your bottom bar and select Task Manager.
- Select Performance. The graph displays the network and link speed for the system.

- Check Network latency from Command Prompt.
- Click the Search icon appearing on the Taskbar of your computer.
- Search for Command Prompt and press Enter.
- Write the command ping server name -t and press Enter.

This instant communication displays ‘Request timed out’ which means you will not be able to access data or your data access will be slow.
For latest Windows systems, click Performance in Task Manager to view the network speed.
For Single user or Server system:
Cause 1:
RAM configuration is different across all the node systems.
Resolution:
Same RAM configuration should be used in all the node systems. For example, if a system has 4 GB RAM with 2.1 GHz processor with Windows 10 Operating System, same configuration to be used across all the nodes.
To check system configuration from TallyPrime, press F1 (Help)> About > Computer Information.
Cause 2:
Different versions of Windows Operating System used across all the node systems.
Resolution:
Windows operating system version should be same in all the node systems. For example, if you are using Windows 10 in one node, then all the systems should have Windows 10.
Cause 3:
Processor speed is different across all the node systems.
Resolution:
Processor speed should be same in all the node systems. If the processor speed is 2.3 Ghz in one node, then the other node systems should also have the same processor speed.
Cause 4:
Existing customisations require additional validation while opening a report.
Resolution:
Try to open the report after deselecting the account TDLs/Add-ons and disabling the local TDLs.
Cause 5:
Memory consumption increases when loading a company, primarily due to the higher data size, which is influenced by the company’s features and the volume of data stored in that company. For example, if a company has 20,000 stock items and 5,000 stock categories, loading the company will use more memory because it checks the balance of each stock item against its category.
Resolution:
Delete the Masters of the company if there are no other masters or transactions using it and try opening the reports again in TallyPrime. In TallyPrime, you can also view and delete multiple unused masters at once.
In client systems/Node:
Cause 1:
RAM configuration is different across all the node systems.
Resolution:
Same RAM configuration should be used in all the node systems. For example, if a system has 4 GB RAM with 2.1 GHz processor with Windows 10 Operating System, same configuration to be used across all the nodes.
To check system configuration from TallyPrime, press F1 (Help)> About > Computer Information.
Cause 2:
Different versions of Windows Operating System used across all the node systems.
Resolution:
Windows operating system version should be same in all the node systems. For example, if you are using Windows 10 in one node, then all the systems should have Windows 10.
Cause 3:
Processor speed is different across all the node systems.
Resolution:
Processor speed should be same in all the node systems. If the processor speed is 2.3 Ghz in one node, then the other node systems should also have the same processor speed.
Cause 4:
Existing customisations require additional validation while opening a report.
Resolution:
Try to open the report after deselecting the account TDLs/Add-ons and disabling the local TDLs.
Cause 5:
Memory consumption increases while opening the report, primarily due to the higher data size, which is influenced by the company’s features and the volume of data stored in that company.
Resolution:
Delete the Masters of the company if there are no other masters or transactions using it and try opening the report again in TallyPrime. In TallyPrime, you can also view and delete multiple unused masters at once.
Cause 6:
Type of network such as LAN or WIFI
Resolution:
Switch the network and try again.
Cause 7:
Slow network speed
Resolution:
Network Speed should be high for example, either 100 Mbps/1Gbps.
Cause 8:
Network cable or the category of cables used, such as Cat 5 or Cat 6/7.
Resolution:
Opt for a cable with higher category value.
Cause 9:
Low bandwidth or unstable network communication between the client and server.
Resolution:
Ping speed variation should be minimal, ideally between 1 ms and 3 ms which is the minimum accepted network variation. Ensure that the network speed is always uniform between the client and the server systems. Any difference in the link speed affects the transfer of data between the client and server system.
For example, when the link speed is 100 Mbps, and the transfer rate is 56 Mbps, the performance of data over the network will be slow. You also need to ensure that the network speed should be 60 Mbps from node to server and server to node systems.
To view the link speed:
- In your computer, right-click on your bottom bar and select Task Manager.
- Click Performance. The graph displays the network and link speed for the system.
- Check Network latency from Command Prompt.
- Click the Search icon appearing on the Taskbar of your computer.
- Search for Command Prompt and press Enter.
- Write the command ping server name -t and press Enter.
This instant communication displays ‘Request timed out’ which means you will not be able to access data or your data access will be slow.
For latest Windows systems, click Performance in Task Manager to view the network speed.
Cause: Higher volume of data present in the company.
Resolution: The data split is a process-oriented and time-consuming activity. Once you start the splitting process, it will not allow the other users to work. So, you are recommended to carry out the data split process after office hours. Try to use a higher system configuration, so that it will be easier and quicker to split your company data. To know more, refer to Split Company Data in TallyPrime.
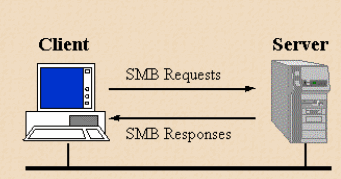
SMB Stands for “Server Message Block.” SMB is a network protocol used by Windows-based computers that allows systems within the same network to share files. It allows computers connected to the same network or domain to access files from other local computers as easily as if they were on the computer’s local hard drive.
Not only does SMB allow computers to share files, but it also enables computers to share printers and even serial ports from other computers within the network. For example, a computer connected to a Windows network could print a document on a printer connected to another computer on the network, as long as both machines support the SMB protocol.
Though SMB was originally developed for Windows, it can also be used by other platforms, including Unix and OS X, using a software implementation called Samba. By using Samba instructions, Mac, Windows, and Unix computers can share the same files, folders, and printers.
SMB Versions
There are several different versions of SMB used by Windows operating systems:
- CIFS – The ancient version of SMB that was part of Microsoft Windows NT 4.0 in 1996. SMB1 supersedes this version.
- SMB 1.0 (or SMB1) – The version used in Windows 2000, Windows XP, Windows Server 2003 and Windows Server 2003 R2
- SMB 2.1 (or SMB2.1) – The version used in Windows 7
- SMB 3.0 (or SMB3) – The version used in Windows 8 and Windows Server 2012
SMB Negotiated Version
Here’s a table to help you understand what version you will end up using, depending on what Windows version is running as the SMB client and what version of Windows is running as the SMB server:
| Client / Server OS | Windows 8 Windows Server 2012 |
Windows 7 | Previous versions of Windows |
| Windows 8 Windows Server 2012 |
SMB 3.0 | SMB 2.1 | SMB 1.0 |
| Windows 7 | SMB 2.1 | SMB 2.1 | SMB 1.0 |
| Previous versions of Windows |
SMB 1.0 | SMB 1.0 | SMB 1.0 |
Features and Capabilities
Here’s a very short summary of what changed with each version of SMB:
- From SMB 1.0 to SMB 2.0 – The first major redesign of SMB.
- Increased file sharing scalability
- Improved Performance
- Request Compounding
- Asynchronous Operations
- Larger reads/writes
- More Secure and Robust
- Small command set
- Signing now uses HMAC SHA-256 instead of MD5
- SMB2 durability
- From SMB 2.0 to SMB 2.1
- File leasing improvements
- Large MTU support
- BranchCache
- From SMB 2.1 to SMB 3.0
- Availability
- SMB Transparent Failover
- SMB Witness
- SMB Multichannel
- Performance
- SMB Scale-Out
- SMB Direct (SMB 3.0 over RDMA)
- SMB Multichannel
- Directory Leasing
- BranchCache V2
- Backup
- VSS for Remote File Shares
- Security
- SMB Encryption using AES-CCM (Optional)
- Signing now uses AES-CMAC
- Management
- SMB PowerShell
- Improved Performance Counters
- Improved Eventing
- Availability
How does SMB work?
The diagram shows the way in which SMB works. Clients connect to servers using TCP/IP. Servers make file systems and other resources (printers, mailslots, named pipes, APIs) available to clients on the network. Client computers may have their own hard disks, but they also want access to the shared file systems and printers on the servers.
Clients connect to servers using TCP/IP (protocol). Once they have established a connection, clients can then send commands (SMBs) to the server that allow them to access shares, open files, read and write files, and generally do all the sort of things that you want to do with a file system. However, in the case of SMB, these things are done over the network.
How SMB impacts performance?
The following table will explain how SMB creates Impact on Performance. The version of SMB used for file sharing is determined during the SMB session negotiation. If both the client and server support SMB 2.0, then SMB 2.0 is selected during the initial negotiation. Otherwise, SMB 1.0 used for preserving backwards compatibility.
Below test was conducted to check the effect on performance.
| Client | Server | SMB Negotiated Version | Effect on performance |
| Win XP | Win 7/win 2008 server | SMB1 | No effect |
| Win 7, Win 2008 server, win xp | Win XP | SMB1 | No effect |
| Win 7, winxp | Win 2008 server/win 7 | SMB2, SMB1 |
Performance effected when first communication is between smb2 to smb2. Performance not effected when first communication is between smb1 and smb1. |
Performance Tests
Test 1: Test using Notepad
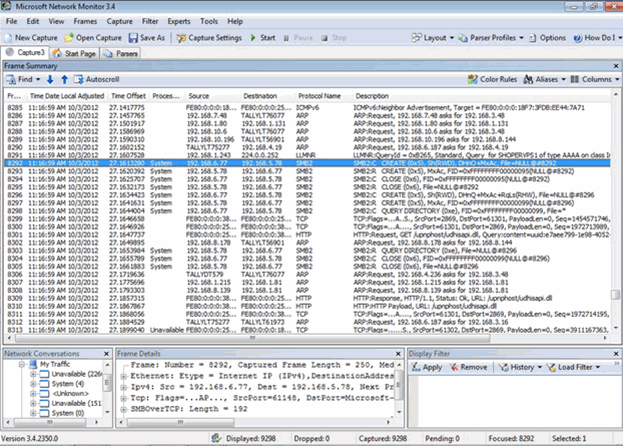
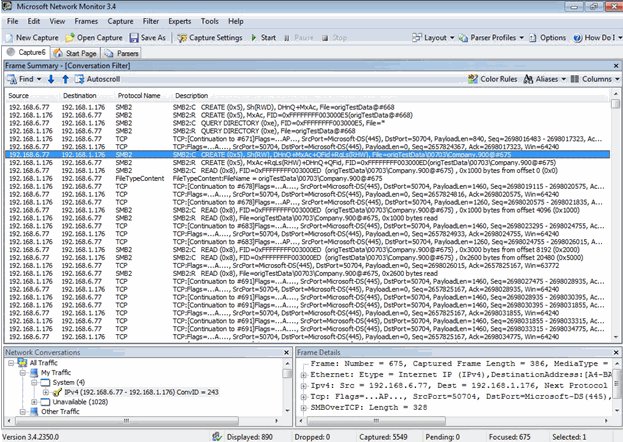
Testing was done by creating a notepad in the shared folder on Win 2008 server. Here the communication happens through smb2 protocol. This can be observed using the Microsoft Network Monitor. (See the highlighted line).
After creating the notepad from Windows 7 try to delete the same from Win XP machine immediately(less than few seconds). On trying to delete, system prompts error message as shown below.
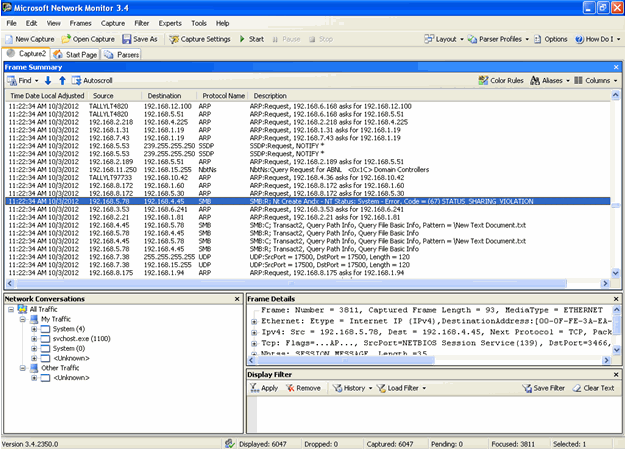
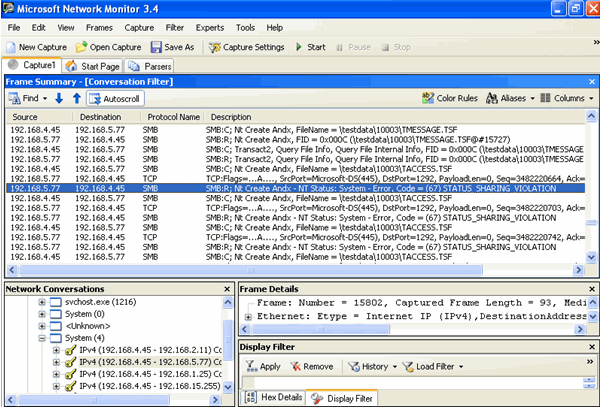
The same can also be observed using the Network monitor, where it shows a Sharing Violation. (See the highlighted line).
Reason
- Client (Windows 7) sends Request to server to Create File via SMB2 (check in Fig 1)
- Server Responses to allow creation for client via SMB2
- After Creation, Client (windows 7) sends request to close SMB2 for the new file created. To sends this request there is a time delay.
- During this delay, if another request comes from SMB1 for accessing the same file then sharing violation error shown. If it is same version of SMB, then able to access the file.
When higher version named pipe is not closed and if request comes from lower version then sharing violation occurs. When lower version client is continuously attempting to access the file then sharing violation happens multiple times. This ultimately impacts the performance of client.
Test 2: Select Company > Display Company Login Screen in Tally.
Testing was done by sharing Tally data folder on win 2008 server. Tally application was opened on window 7 and company was selected to display the Login Screen. During this process the SMB2 protocol is used to communicate with the windows server 2008 machine.
Then the same data was accessed by WinXP via SMB Protocol. From the Win XP client, to display the Login screen of the same Company, it is taking time.
In the Network Monitor, it is continuously showing sharing violation in TAccess.tsf file.
Reason
- Client (Windows 7) sends Request to server to Create TAccess.tsf File via SMB2
- Server Responses to allow creation for client via SMB2
- After Creation, Client (windows 7) sends request to close SMB2 for TAccess.tsf file. To sends this request there is a time delay.
- During this delay time, Windows XP sends request to server for creation of TAccess.tsf file. Since SMB2 namedpipe is not closed for TAccess.tsf file in Windows 7 client, it is showing sharing violation in WinXP client.
Tally Application in WinXP client will wait until it gains access to the TAccess.tsf file. This wait time impacts performance.
Conclusion
From the tests, we can conclude that in a sharing environment, the performance will be impacted when data server is in higher SMB version and Clients are in both higher and lower SMB Versions.
Recommendation
Option 1
- Data Server – SMB1 Version OS
- Clients – (SMB 1 or higher Version OS)
- As Data server is in SMB1, communication will happen in SMB1 only.
Option 2
- Data Server – SMB2 Version OS
- Clients – (SMB 2 or higher Version OS)
- As Data Server is in SMB2, Communication will happen in SMB2 Only.
Option 3
- Data Server – SMB3 Version OS
- Clients – (SMB 3 or higher Version OS)
- As Data Server is in SMB3, Communication will happen in SMB3 Only.