Costing Methods and Market Valuation Methods | Stock Valuation Methods
Costing methods enable you to identify the worth of your business inventory at any point in time. Market Valuation Methods help you to auto-fill the selling price of the items while recording sales. TallyPrime provides the flexibility to compare stock values arrived from different costing methods, and define selling prices based on various valuation methods.
Being on top of the assets and worth of your business is very critical at any point in time. The worth of your assets will vary based on different factors like inflation, deflation, environmental changes, depreciation, and so on. One of the important assets that you possess is inventory. In the case of the value of your inventory, apart from the factors mentioned here, costing methods also play a crucial role. You can select a costing method at the beginning of a financial year. If you are a private limited company and you want to change the current method, you must list valid reasons to your stakeholders and with the collective decision you can change the method to be used in the upcoming financial year.
Similarly, it is essential that the stock items are sold at a price that will be profitable for your business. TallyPrime offers market valuation methods for these purposes. Depending on the market valuation method you choose, you will be able to auto-fill the selling price of the stock items during sales. Applying the correct market valuation method will help you in determining the most beneficial selling price for the stock, and enhance the profitability of your business.
The closing stock impacts your books of accounts. Therefore, at the end of a financial year, you should be able to identify how much stock is available and what it is worth. TallyPrime helps you in determining the net worth of your stock at any given time and enables you to accurately represent the inventory value in the financial statement of your company. TallyPrime not only assists you in evaluating your inventory but also helps to do comparative analysis based on various stock valuation methods. You need to create columns and show valuation methods with changes in closing value. Reports such as Balance sheet, Profit & Loss A/c where the closing stock value is shown we can create columns for comparison. The comparison also can be done in these reports. Any valuation method applied at the master level will be considered to show closing stock values. When applying for a loan for your business or looking for potential investors, you need to project the best valuation of your closing stock for these aspects. While the quantity of unsold items would remain unchanged its value might vary based on the costing method you choose. Reports in TallyPrime provide flexibility to compare and contrast the stock values to assist you in making the right decisions. Costing methods like average cost, LIFO, standard cost, FIFO and others will help you in determining what is the value of your stock items. In TallyPrime, Average Cost is selected as the default costing method.
Similarly, the market valuation methods such as average price, zero price, last sale price and the rest will help you determine the price at which your stock needs to be sold to run the business in a healthy manner. In TallyPrime, the Average Price is used as the default market valuation method. You can change this as desired.
You can select stock valuation methods in TallyPrime from the Basis of Values in reports such as Stock Ageing Analysis, Stock Summary, Balance Sheet, Profit and Loss and so on to see the impact if you change the valuation method.
Costing Methods
TallyPrime offers you varied costing methods that will help you in determining the value of the stock in hand. You can know the worth of your inventory by selecting the suitable costing method as per your business requirements. Every stock item can be set up to have a different costing method if needed.
Depending on which method will provide better outcomes for your company, you can select any of the following costing methods at the beginning of a financial year.
- At Zero Cost
- Average Cost
- FIFO (First In, First Out)
- FIFO Perpetual
- Last Purchase Cost
- LIFO Annual (Last In, First Out)
- LIFO Perpetual
- Standard Cost
- Monthly Average Cost
At Zero Cost
Under this costing method, the value of stock items will always be zero, irrespective of the cost incurred. No matter what amount you have paid for procuring the stock items, their cost will not be listed and only the quantity will be shown in the book of accounts. This can be used for all consumables for which you don’t want to project the value in your books.
Average Cost
In TallyPrime, this is the default costing method for deciding the value of the stock in hand. If items you deal with in your business have fluctuating price trends, it is difficult for you to adopt the best valuation method. In such a case you can use the Average Cost valuation method to get the best results.
Suppose you purchased varied quantities of pencils at different rates across a period of time. The average cost of purchasing the pencils can be calculated as follows.
| Date | Quantity (in boxes) | Rate | Amount |
| 10.04.2022 | 100 | 120 | 12000 |
| 20.08.2022 | 100 | 150 | 15000 |
| 30.11.2022 | 200 | 200 | 40000 |
| 10.02.2023 | 100 | 150 | 15000 |
| Total | 500 | 82000 |
Average Cost = Total Cost/Total Quantity
= 82000/500
= 164
The value of the remaining stock can be calculated by multiplying the average cost with the quantity of the remaining stock.
FIFO (First In First Out)
This method is mostly applied when the first item that you purchase, or produce is the first one to be sold off. The older items are sold first which indicates that the remaining stock items after the sales, are from the most recent purchase or production. If the price of the item is increasing and you select the FIFO method for valuation, the value of closing stock inflates. That means the value of the remaining stock becomes higher.
Consider that you purchase and sell headphones and want to know the worth of the stock-in-hand.
| Date | Transaction Type | Quantity | Rate | Closing Stock |
| 01.04.2022 | Purchase | 50 | 500 | 50 |
| 30.06.2022 | Sales | 20 | 550 | 30 (@500) |
| 30.09.2022 | Sales | 10 | 555 | 20 (@500) |
| 10.10.2022 | Purchase | 80 | 520 | 100 (20@500 & 80@520) |
Value of the closing stock = Respective purchase cost * Closing quantity
= 20*500+80*520
= 51,600
On selecting this method, the leftover stock will be valued using the respective purchase cost as the reference.
When using this method, the calculated value of stock gets carried forward in your books. At the same time, the stock remaining at hand may be from current batches. Also, the cost of the opening stock in the new year will be calculated as an average as shown below.
Cost of the opening stock = 51600/100
= 516
FIFO Perpetual
This valuation method is used when you are reporting inventory usage on a multi-year basis. If you have a company running for more than a year, on selecting this costing method, the stock valuation will be from the time the Company was created in Tally.
On selecting this method, the leftover stock will be valued using the last purchase price as the reference. Hence, if the price of the item is increasing year-on-year the value of closing stock inflates, regardless of the fact that stock is from a previous year.
When using this method, the quantity of stock gets carried forward in your books and the value of the stock is calculated based on the last (most recent) purchase price as the reference.
Last Purchase Cost
When the inventory valuation is based on the last purchase cost at which you procured the items, this method is used. Let’s suppose that you have made multiple purchases of an item on different days at varied rates. The inventory will be valued based on the last purchase cost of that item.
Here, the items may not be sold on a first-in first-out basis. Hence, stock from an older batch will also get valued at the latest purchase cost.
For instance, you purchased sneakers at varied rates over a period of time. While valuing the stock-in-hand, the rate at which you made the last purchase will be taken into account and the remaining items will be valued accordingly.
| Date | Transaction Type | Quantity | Rate | Closing Stock |
| 06.04.2022 | Purchase | 50 | 520 | 50 |
| 30.06.2022 | Sales | 30 | 550 | 20 |
| 10.08.2022 | Purchase | 100 | 540 | 120 |
| 10.10.2022 | Purchase | 80 | 530 | 200 |
| 31.12.2022 | Sales | 70 | 560 | 130 |
Value of the closing stock = Last purchase cost * Closing quantity
= 530*130
= 68900
On selecting this method, the leftover stock will be valued using the last batch of purchases as the reference. The value of the remaining sneakers will be calculated by multiplying the quantity of the remaining stock with the rate at which the last batch of sneakers was purchased.
LIFO Annual (Last In First Out)
As opposed to the FIFO method, under this method, the last stock items that were purchased or produced are sold off first. This indicates that the stock-in-hand may be from any older batches.
Whether the price of stock items follows an increasing or a decreasing trend if you have selected the LIFO method, the value of the closing stock remains stable at the respective purchase costs.
Consider that you purchase and sell slippers and want to know the value of the stock in hand.
| Date | Transaction Type | Quantity | Rate | Closing Stock |
| 05.05.2022 | Purchase | 200 | 200 | 200 |
| 10.05.2022 | Sales | 100 | 250 | 100 (@200) |
| 15.05.2022 | Purchase | 100 | 190 | 200 (100@200 & 100@190) |
| 20.05.2022 | Sales | 50 | 220 | 150 (100@200 & 50@190) |
Value of the closing stock = Respective purchase cost * Closing quantity
= 100*200+50*190
= 29500
On selecting this method, the leftover stock will be valued using the respective purchase cost as the reference.
When using this method, the calculated value of stock gets carried forward in your books. At the same time, the stock remaining at hand may be from older batches. Also, the cost of the opening stock in the new year will be calculated as an average as shown below.
Cost of the opening stock = 29500/150
= 196.67
LIFO Perpetual
This valuation method is used when you are reporting inventory usage on a multi-year basis. If you have a company running for more than a year, on selecting this costing method the stock valuation will be from the time the Company was created in Tally.
In this method, the earliest entry of inventory in the system is considered as the first batch even if the entry was made 10 years ago. On selecting this method, the leftover stock will be valued using the respective purchase cost as the reference.
When using this method, the quantity of stock gets carried forward in your books and the value of the stock is calculated based on the respective purchase cost as the reference. Also, the stock remaining at hand may be from older batches.
Standard Cost
This valuation method determines the cost of stock items once a standard or predetermined cost is set. Once you define the Standard Cost, the rate is applicable for the inventories irrespective of the price of purchase or production. This method assigns a predetermined cost to every unit of the item such as material cost, labour, overhead prices, production costs, freight charges, packaging and so on. The frequent purchases of the item at different rates would not make a difference in the value of the inventory.
By identifying the difference between actual costs and standard costs, you will be able to manage finances and reduce wasteful spending on resources. This method provides accuracy in financial reporting. Companies that have to budget the cost of any item that is required to assemble the final product can benefit from this valuation method.
Suppose you make sweatshirts, and the rate at which you purchased the items varies with time. You may incur expenses as shown in the table below.
| Date | Quantity | Cost per Item | Total Amount |
| 01.04.2022 | 10 units | 300 | 3000 |
| 02.06.2022 | 20 units | 350 | 7000 |
On 1st October, you decided to define the standard cost as Rs 500. Therefore, once the Standard cost is determined, the remaining stock will be valued at 500. If you have 30 units remaining in total, then the value will be 30*500=15,000.
Monthly Average Cost
In the monthly average costing method, the closing value of each month will be treated as an opening for the next month. The average cost for purchasing the stock items will be calculated on a monthly basis and the value of the stock items is based on this calculation.
Market Valuation Methods
With the various valuation methods offered by TallyPrime, you will be able to determine the best sale price for your stock items.
The following methods will help you in setting appropriate selling rates for your closing stock.
At Zero Price
If you select this valuation method, by default there will be no rate included when recording the voucher. You have to decide the price at which you should sell each item and key in the rate.
Average Price
Using this method, you will be able to derive the average rate at which you will sell the stock item and yield maximum profit. The average price for selling the stock items is calculated by dividing the total amount at which the stock items were sold by the total quantity of the item sold so far.
In TallyPrime, this is the default valuation method for deciding the price at which stock items may be sold.
Initially, you will have to key in the rate at which you will sell the stock item. Later on, TallyPrime will calculate the average price for the item and show it in the invoice. Whenever you want to change the rate, you can key in a different rate. Going forward, the average price will be calculated considering the revised rates too.
Assume that you are selling ball pens at varied rates over a period of time.
| Date | Quantity | Rate | Amount |
|
10.10.2022 (first sale) |
10 |
10 (keyed in) |
100 |
|
20.10.2022 (second sale) |
10 |
12 (keyed in) |
120 |
|
30.10.2022 (third sale) |
15 |
11 [calculated as (100+120)/20] |
165 |
|
08.11.2022 (fourth sale) |
15 |
14 (keyed in) |
210 |
|
10.12.2022 (fifth sale) |
10 |
12.5 [calculated as (100+150+165+210)/50] |
125 |
The selling price of the stock item is calculated by multiplying the average price and the quantity.
Last Sales Price
Under this method, the selling price of the stock item is based on the last price at which the stock item was sold. When you make multiple sales of the same product over a period of time, due to reasons such as inflation, seasonal variation, increase in demand, limited availability, and so on, the price of the product may fluctuate. In this case, the last sale price will be shown for reference while deciding the selling price of the stock item.
Initially, you will have to key in the rate at which you will sell the stock item. Later on, TallyPrime will show the last selling price for the item in the voucher. Whenever you want to change the rate, you can key in a different rate.
Consider that you have sold sneakers at varied rates over a period of time. The following table shows the last sales price that TallyPrime shows in the voucher.
| Date | Quantity | Rate Displayed | Rate Entered | Amount |
|
25.06.2022 (first sale) |
50 | — | 400 | 20000 |
| 30.11.2022 | 100 | 400 | 450 | 45000 |
| 13.12.2022 | 200 | 450 | — | 90000 |
| 25.12.2022 | 150 | 450 | 500 | 75000 |
On selecting this valuation method, the price at which the sneakers were sold earlier will be prefilled in the voucher. You can change the selling price as required.
Standard Price
You can set standard prices for the stock items. The standard price of an item is set after adding charges like the cost of raw materials, production costs and other overhead charges that were required to make the final product.
Suppose you sell jute bags and due to the increasing price of jute, you decide to increase the price of the jute bags. After adding the overhead charges, you list the items for sale based on the set standard price. Thereafter, the sale will be done as per the prevailing standard price.
| Date | Quantity | Rate per Item | Amount |
| 01.09.2022 | 30 | 300 | 9000 |
| 10.12.2022 | 50 | 400 | 20000 |
| 03.03.2023 | 50 | 550 | 27500 |
In this case, the sale will be at the rate of 300 until 10.12.2022. Then, the rate will change to 400 and will continue till 03.03.2023. Thereafter, the rate will change to 550.
Stock Valuation Method in TallyPrime
In TallyPrime, you can decide the costing method to be used for the closing stock along with the Market Valuation method of the stock items. You need to configure the stock item and select the Costing Method and the Market Valuation Method to be used for that particular stock item. Additionally, you can compare the closing stock value depending on the stock valuation methods. Such comparisons can be done from reports where the value of closing stock appears such as Balance Sheet, Profit & Loss A/c. You need to create Auto Column and select Stock Valuation Methods which will reflect the value of closing stock for all the valuation methods. This comparison will help you to take better decisions on the valuation of the stock. Apart from these, you can also define Standard Rates for your stock items. Once the standard rates are defined you can sell the stock items with the predetermined rates. These standard rates can be maintained on a daily basis or for a period.
In this section
- Changing valuation method for a Stock Item
- Compare valuation methods in the report
- Defining Standard rates
Changing valuation method for a Stock Item
In order to decide the stock valuation method to be used for determining the closing stock value for your business or to decide the Market Valuation Method for stock items you can configure the stock items with these details.
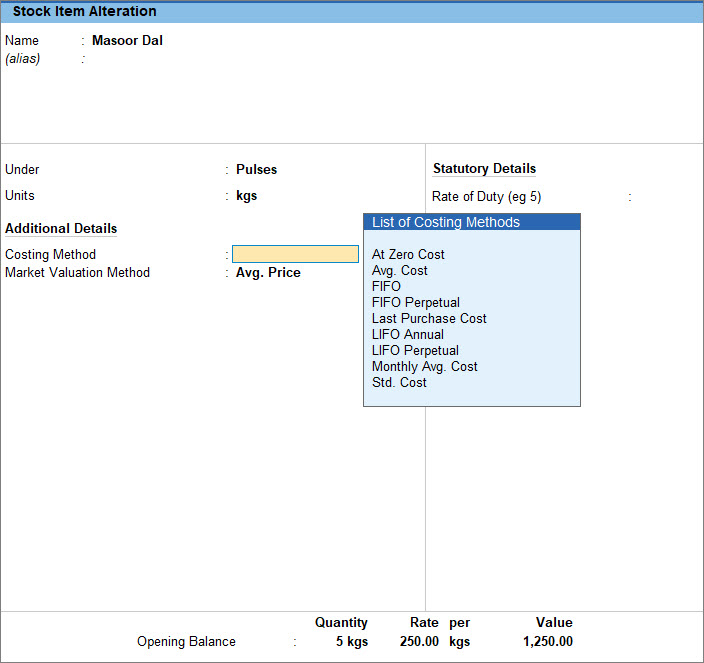
![]()
- Press Alt+G (Go To) > Alter Master > Stock Item > type or select Stock Item > press Enter.
Alternatively, Gateway of Tally > Alter > Stock Item > type or select Stock Item > press Enter. - Press F12 (Configure) and enable Use Costing and Market Valuation Methods for Stock Items.
If you do not see this option: - Accept the screen. Press Ctrl+A to save the Stock Item Alteration screen.
Now you can define Costing Methods and Market Valuation Methods for the stock item.
Compare valuation methods in the report
You can compare the value of your closing stock based on different valuation methods and you can take a decision as to which valuation method to be used for the next financial year. The below procedure is to view the comparison from the Balance Sheet.
- Press Alt+G (Go To) > type or select Balance Sheet > press Enter.
Alternatively, Gateway of Tally > Balance Sheet > press Enter. - Press Alt+N (Auto Column) and select Stock Valuation Methods.
Balance Sheet appears with various Stock Valuation Methods. - Press Alt+F5 (Detailed) to see the detailed view.
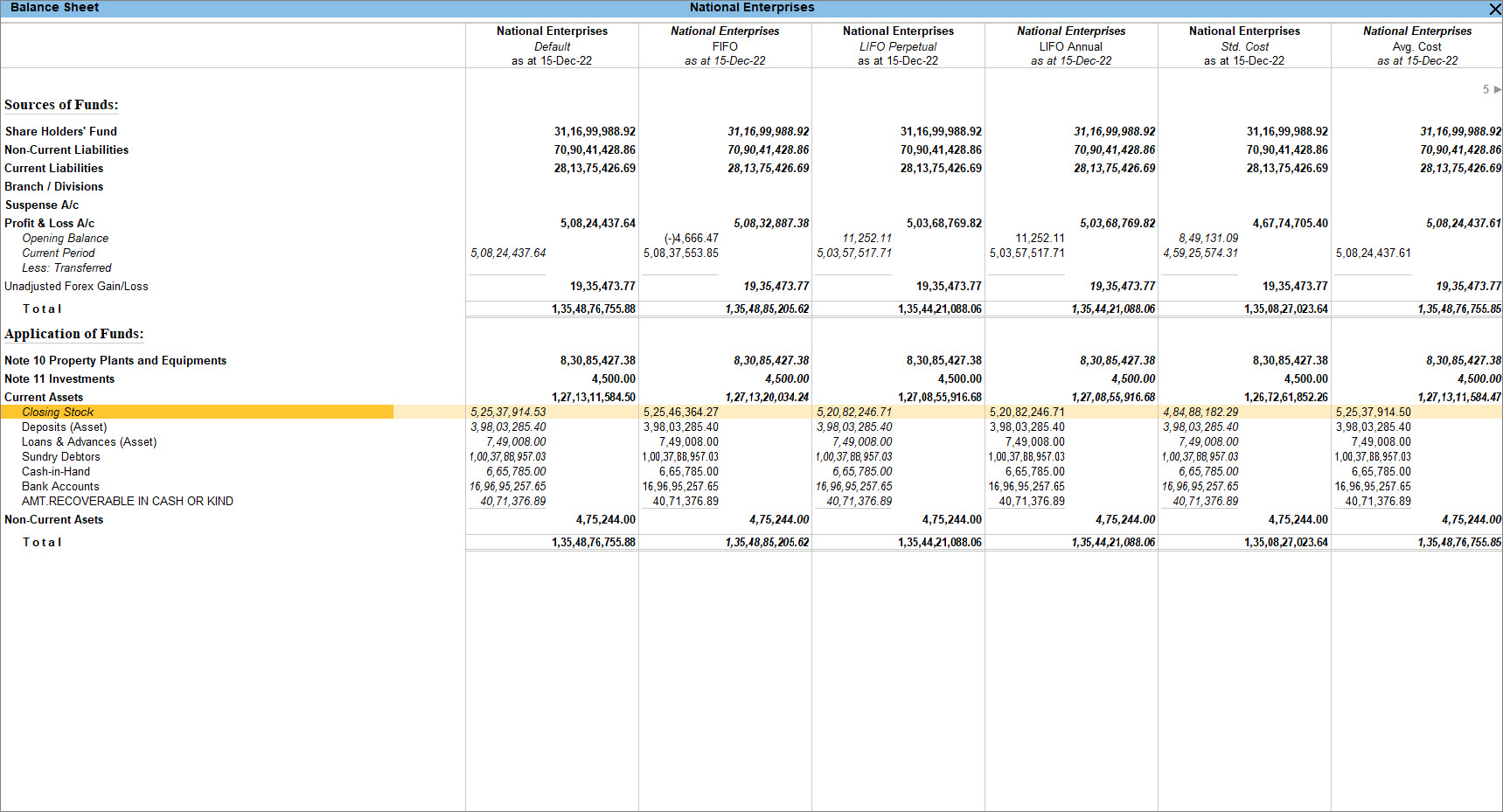
The comparative study of the closing stock value based on the different valuation methods will help you to decide the stock valuation method to be implemented in the next financial year.
Defining Standard rates
You can define the standard rate for your stock items daily by entering the date for a stock item. You can also specify the standard rates for a period.
- Create or Alter stock item and configure standard rates.
- Press Alt+G (Go To) > Create Master/Alter Master > Stock Item > press Enter.
Alternatively, Gateway of Tally > Create/Alter > Stock Item > press Enter. - Press F12 (Configure) > set the option Provide Standard Buying and Selling Rates to Yes.
If you do not see the above option, set Show more configurations to Yes. - Accept the configuration screen.
- Press Alt+G (Go To) > Create Master/Alter Master > Stock Item > press Enter.
- In the Stock Item Alteration screen, set the option Alter standard rates to Yes.
- Enter the Standard Cost and Standard Selling Price with the Applicable From date and Rate per unit.
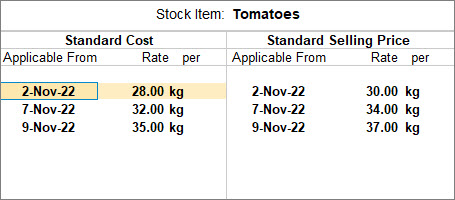
- Accept the screen. Press Ctrl+A to save the screen.
For more details on how to use Standard rates click here.